Grounded Theory on the Strength of Curriculum Development Systemin Demonstration Secondary School, Khon Kaen University
Keywords:
Grounded theory, Curriculum development system, CurriculumAbstract
This was qualitative research in the form of grounded theory. The purpose of this research was to present a theoretical conclusion from the strength of the curriculum development system at Demonstration Secondary School. The key informants included administrators, the curriculum development and learning management committee, the head of the learning group, and lecturers, totaling 6 people. The instrument was an in-depth interview with guided questions that included 1) basic information of key informants, 2) teaching and learning management, 3) school administration and management, 4) strengths and weaknesses of the curriculum development system, and 5) suggestions. The data were collected by transcripts of key informants’ interviews. The data were encoded and analyzed using ATLAS.ti program which can analyze unstructured data through coding.
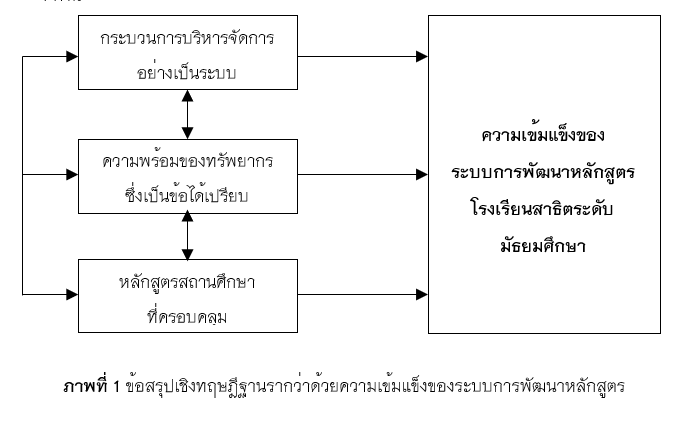
The result found that the strengths of the curriculum development system in the Demonstration Secondary School are in 3 dimensions, including 1) a systematic management process, 2) the availability of resources is an advantage, and 3) a comprehensive school curriculum.
References
กระทรวงศึกษาธิการ. (2565). นโยบายและจุดเน้น ของกระทรวงศึกษาธิการ ปีงบประมาณ พ.ศ.2565. กรุงเทพฯ: กระทรวงศึกษาธิการ.
คมกฤช ตาชม และ สนิท ยืนศักดิ์. (2561). ทัศนคติและการทำวิจัยปฏิบัติการในชั้นเรียนของครูภาษาอังกฤษ. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา, 6(1), 21-41.
ชนมณี ศิลานุกิจ, อำนวย ทองโปร่ง, รังสรรค์ มณีเล็ก, และ สุวัฒน์ วิวัฒนานนท์. (2563). รูปแบบการบริหารโรงเรียนโดยใช้วงจรคุณภาพ สังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษา ประถมศึกษากรุงเทพมหานคร. วารสารดุษฎีบัณฑิตทางสังคมศาสตร์, 10(1), 43-58.
ณิชกานต์ แก้วจันทร์ และ ธนินท์รัฐ รัตนพงศ์ภิญโญ. (2564). ความพร้อมในการจัดการเรียนการสอนและความคาดหวังประสิทธิผลการศึกษาในระบบการเรียนการสอนออนไลน์ ในทรรศนะของนักศึกษาคณะวิทยาการจัดการ มหาวิทยาลัยศิลปากร. (วิทยานิพนธ์ศึกษาศาสตร์มหาบัณฑิต). กรุงเทพฯ: มหาวิทยาลัยศิลปากร.
นพวรรณ เมืองแก้ว และ กนกวรรณ วารีเขตต์. (2566). การวิเคราะห์ลักษณะและโครงสรางของ ปริจเฉทรายการวิทยุคลับฟรายเดย์. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา, 11(1), 46-66.
พัชมณ สระแก้ว, ปิยาภรณ์ ศิริภานุมาศ และ สุรชัย ปิยานุกูล (2560). ปัญหาและแนวทางแก้ปัญหาการบริหารงานวิชาการของโรงเรียนขนาดเล็ก สังกัดส านักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษามัธยมศึกษาบุรีรัมย์ เขต 32. การประชุมวิชาการเสนอผลงานวิจัยบัณฑิตศึกษา ระดับชาติและนานาชาติ 2560. ขอนแก่น: มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น.
วรัญญา ยิ่งยงศักดิ์. (2561). การใช้ภาษาในการเสนอภาพสตรีจากนิตยสารบันเทิงไทย. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา, 6(2), 140-152.
วรางคณา สุพรรณชนะบุรี และ อลิสา คุ่มเคี่ยม. (2565). วาทกรรมความรักจากเพจ Coach Jibb. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา, 10(2), 102-118.
วันทนีย์ ศรีบุรินทร์ และ จุไรรัตน์ อาจแก้ว. (2562). การวิเคราะห์องค์ประกอบคุณลักษณะการเป็นบุคคลแห่งการเรียนรู้ในศตวรรษที่ 21 ของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 3 สังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษาเลย เขต 1. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา, 7(2), 1-23.
วารีรัตน์ แก้วอุไร. (2564). การพัฒนาหลักสูตร: จากทฤษฎีสู่การปฏิบัติ. พิษณุโลก: สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร.
วุฒิพงษ์ ศรีจันทรี, จํานงค์ แจ่มจันทรวงษ์ และ วีรพันธุ์ ศิริฤทธิ์. (2561). ทักษะการบริหารสถานศึกษาในศตวรรษที่ 21 ของผู้บริหารสถานศึกษาสังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษาเชียงรายเขต 2. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา, 6(2), 124-139.
ศิวะลักษณ์ มหาชัย และ เอกราช โฆษิตพิมานเวช. (2565). การพัฒนาหลักสูตรสถานศึกษา. วารสารมณีเชษฐาราม วัดจอมมณี, 5(2), 168-185.
สำนักงานสภาพัฒนาการเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งชาติ สำนักนายกรัฐมนตรี. (2565). แผนพัฒนาเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งชาติ ฉบับที่ 13 (พ.ศ. 2566-2570). ราชกิจจานุเบกษา, จากhttp://www.ratchakitcha.soc.go.th/DATA/PDF/2565/E/258/T_0001.PDF.
สุภัค ยมพุก และ วิโรจน์ เจษฎาลักษณ์. (2558). การบริหารสถานศึกษาและการรับรู้การสนับสนุน การปฏิบัติงานที่ส่งผลต่อประสิทธิผลการสอนของครูโรงเรียนมัธยมศึกษา สังกัด สำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษามัธยมศึกษา เขต 1 กลุ่มที่ 4. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์ สังคมศาสตร์ และศิลปะ, 8(2), 78.
สุรีรัตน์ ยอดบุรี และ นิคม นาคอ้าย. (2564). การศึกษาปัญหาและแนวทางพัฒนาการบริหารหลักสูตรสถานศึกษาของโรงเรียนขนาดเล็กสังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษากำแพงเพชร เขต 1. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 7(1), 289–303.
Charmaz, K. (2009). Constructing Grounded Theory: A Practical Guide Through Qualitative Analysis. Los Angeles London: SAGE.
Cullen, M. M., & Brennan, N. M. (2021). Grounded Theory: Description, Divergences and Application. Accounting, Finance & Governance Review, 27, from https://doi.org/10.52399/001c.22173.
Ghonoodi, A., & Salimi, L. (2011). The Study of Elements of Curriculum in Smart Schools. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 28, 68-71, from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.014.
Howard, J. (2007). Curriculum Development. Center for the Advancement of Teaching and Learning Elon University, from https://www.uwindsor.ca/ctl/sites/uwindsor.ca.ctl/files/curriculum-development.pdf.
KKU Archives. (2546). ระเบียบมหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่นว่าด้วยการศึกษาของโรงเรียนสาธิต มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น, จากhttps://archive.kku.ac.th/omeka/items/show/5078.
Moen, R., & Norman, C. (2009). Evolution of the PDCA Cycle. Proceedings of the 7th ANQ Congress, Tokyo 2009.
Xia, S. (2020). Developing Awareness of Questioning Strategies for Second Language Learner Teachers. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 11(6), 853, from https://doi.org/10.17507/jltr.1106.01.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Phayao University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยาไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย
The authors are themselves responsible for their contents. Signed articles may not always reflect the opinion of University of Phayao. The articles can be reproduced and reprinted, provided that permission is given by the authors and acknowledgement must be given.







