From an Integration of Linguistics to an Alteration of Attitudes towards English Language Teaching and Learning
Keywords:
Attitude, Integrated instruction, Phonics, Semantic Field, SyntaxAbstract
This research article aims to investigate both teacher’s and students’ attitudes towards linguistic integration concept associated with English teaching and learning. The purposively sampling included an English teacher and her 12 students of Grade 4 in Betty Dumen Border Patrol Police School in Pong Sub-district, Phayao province. After the implementation of
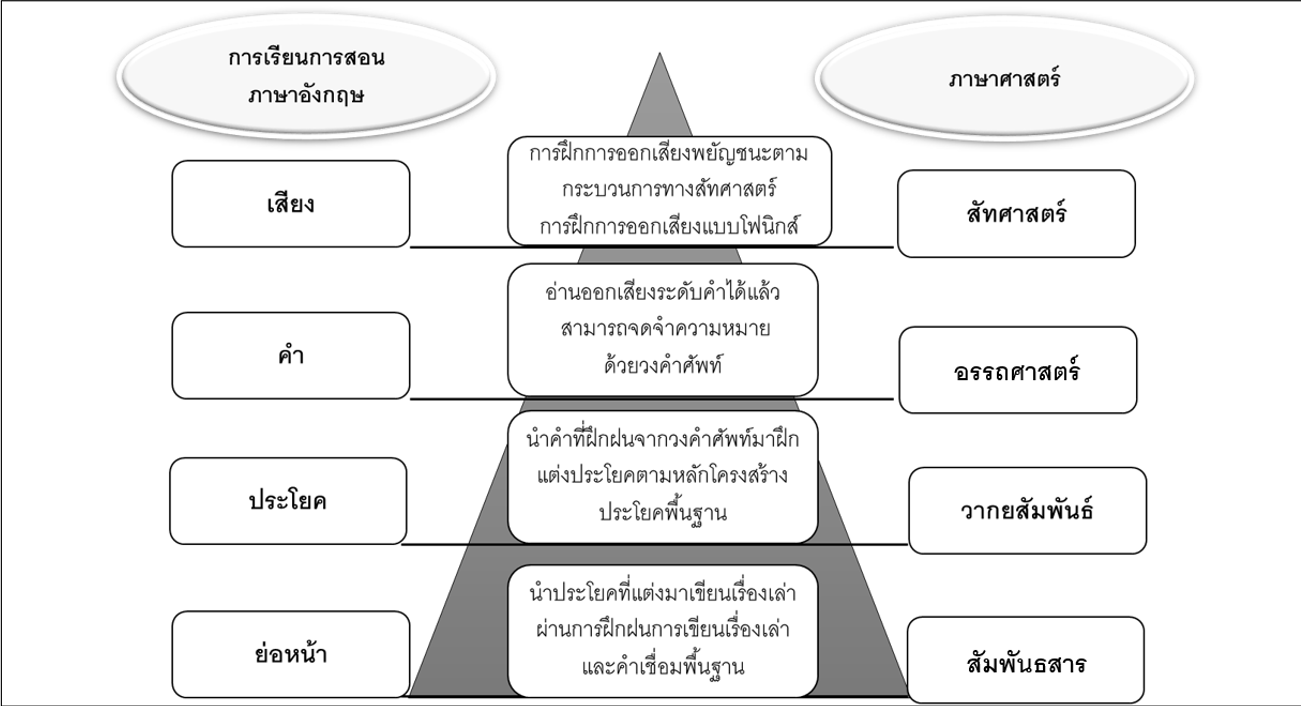
the teaching, the questionnaires consisted 2 parts: attitudes towards the teaching and further comments were distributed to the teacher and the students. Mean and Standard Deviation were used to analyse data. The research results are divided into 2 parts, the attitude of teacher and students towards integrated English language teaching and additional suggestions and comments. With regard to attitude towards the teaching and integrated learning, teacher’s level of attitude was highest (x̅= 4.70, S.D. = 0.48) as well as the students’ attitude with highest level (x̅= 4.51, S.D. = 0.22). In the part of attitude towards English language teaching and learning, teacher showed their highest level of attitude (x̅= 5, S.D. = 0) whereas the students’ level of attitude was high (x̅= 4.40, S.D. = 0.20). In the aspect of suggestions and opinions towards integrated learning and teaching, teacher viewed integrated learning and teaching was beneficial to learners, particularly drawing her students’ attention and learning development, whereas the students viewed this method of teaching helped them learn and improve their learning development, both in pronunciation vocabulary recognition and writing at the sentence to paragraph level.
References
นันทพร คชศิริพงษ์. (2541). การเปรียบเทียบผลสัมฤทธิ์และความคงทนในการเรียนรู้คําศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษระดับมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 1 จากการสอนโดยใช้แบบฝึกหัดที่มีเกมและไม่มีเกมประกอบ. (การศึกษามหาบัณฑิต (หลักสูตรและการสอน), มหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒประสานมิตร, กรุงเทพฯ.
เพ็ญนภา คล้ายสิงห์โต, อภิญญา ห่านตระกูล, นริศา ไพเจริญ, พิชญ์สินี เสถียรธราดล, & ดารินทร อินทับทิม. (2562). การพัฒนาการเรียนการสอนด้วยการบรูณาการทางภาษาศาสตร์. มุทิตาปริทรรศน์. ชุดแนวทางพัฒนาการเรียนการสอนในยุค THAILAND 4.0 สู่ผลลัพธ์ที่จับต้องได้ เนื่องในโอกาสการเกษียณอายุราชการของ รองศาสตราจารย์ พูนพงษ์ งามเกษม (พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1 ed.). คณะศิลปศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา: คณะศิลปศาสตร์.
ศิร แสงธนู, & คิด พงษ์ทัต. (2541). คู่มือภาษาอังกฤษภาคทฤษฎีและปฏิบัติ. กรุงเพทฯ: ไทยวัฒนาพานิช.
เหงียน ถิ หญือ อี๊. (2556). การใช้เกมคำศัพท์เพื่อพัฒนาการเรียนรู้คำศัพท์ภาษาไทยของนักศึกษาชั้นปีที่ 1 มหาวิทยาลัยสังคมศาสตร์และมนุษยศาสตร์ นครโฮจิมินห์ สาธารณรัฐสังคมนิยมเวียดนาม. (ศิลปศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต), มหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒ, กรุงเทพฯ.
อภิญญา ห่านตระกูล และคณะ. (2562). รายงานความก้าวหน้าโครงการวิจัยรอบ 6 เดือน โครงการพัฒนาทักษาภาษาอังกฤษของนักเรียนชั้นประถมศึกษาปีที่ 4 ผ่านการบูรณาการวิธีการสอนแบบโฟนิกส์เข้ากับการพัฒนาวงศัพท์และวากยสัมพันธ์เพื่อสร้างสัมพันธสารเรื่องเล่าเกี่ยวกับประสบการณ์ท้องถิ่น. รายงานการวิจัย. สำนักงานกองทุนสนับสนุนการวิจัยและมหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา.
Akhiar, A., Mydin, A.-A., & Kasuma, S. A. A. (2017). Students’ perceptions and attitudes towards the use of Instagram in English language writing. Journal of Education, 47, 72.
Al Darwish, S. (2017). Teachers’ attitude toward a foreign language: Factors affecting the target language teaching process. International Journal of English Language Teaching, 5(1), 1.
Ardeshir, D., & Shirkhani, S. (2015). Students' Attitudes towards the Use of Poetry in Second Language Classrooms. Journal on English Language Teaching, 5(2), 28-33.
Behroozian, R., & Sadeghoghli, H. (2017). A Study of Students’ Attitudes toward Using Technology in Second Language Learning. Journal of Applied Linguistics Language Research, 4(8), 201-216.
Blasco, D. (2016). Student’s attitudes toward integrating mobile technology into translation activities. International Journal on Integrating Technology in Education, 5(1), 1-11.
Changhong, G. (2010). The Application of the Semantic Field Theory in College English Vocabulary Instruction. Chinese Journal of Applied Linguistics, 33(4).
Disayapong, I. (2015). Thai Primary English Teachers’ Attitudes toward Content-based Instruction. (Degree of Master of Arts in Teaching English as a Foreign Language), Thammasat University.
Elliott, K. (2015). Phonics for young language learners. Retrieved from http://www.cambridge.org/elt/blog/2015/05/phonics-young-language-learners/
Englishfun. (2018). Teaching Vocabulary. Retrieved from http://sites.goolge.com/site/rianlanguages/kar-sxn-kha-saphth
Goe, A. D. (2012). A study of students and teachers’ attitudes towards the integrated syllabus of English in Secondary schools in Mombasa District. (Master’s Thesis of Education), Kenyatta University, Kenya.
Hashemi, M. (2011). Language stress and anxiety among the English language learners. Procedia-Social Behavioral Sciences, 30, 1811-1816.
Horwitz, E. K., Horwitz, M. B., & Cope, J. (1986). Foreign language classroom anxiety. The Modern language journal, 70(2), 125-132.
Klassen, K. J., & Willoughby, K. A. (2003). In-class simulation games: Assessing student learning. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 2, 1-13.
KM Eshreteh, M., & Hisham Siaj, A. (2017). Attitudes of english-major students and teachers towards using blended learning in the english department at Hebron University. International Journal of Research in English Education, 2(4), 51-65.
Lucarevschi, C. R. (2016). The role of storytelling on language learning: A literature review. Working Papers of the Linguistics Circle, 26(1), 24-44.
Lyons, J. (1977). Semantics Vol.1. London: Cambridge University Press.
Mackey, W. F. (1967). Language Teaching Analysis. London: Green Co., Ltd.Marion.
Panjaluck, T. (2014). A Study of English Vocabulary Achievement and Retention of Prathomsuksa Five Students at the Elementary Demonstration, School of Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University by Using Reading Plus Vocabulary. Enhancement Activities. Journal of Multidisciplinary in Social Sciences, 10(2), 55-72.
Richards, L. (1996). Teacher learning in language teaching. New York: McGraw - Hill.
Saeed, J. I. (2009). Semantics. UK: Wiley-Blackwell.
Sulaiman, O. I. (2017). The Attitudes of English Teachers toward Educational Technology in Teaching English and their Relation to the Degree of its Utilization in Primary Schools in the Governorate of Baghdad. (Master’s Thesis in Curricula and Teaching Methods), Educational Sciences Middle East University, Amman – Jordan.
Thuy, N. N. (2013). The effects of semantic mapping on vocabulary memorizing. Paper presented at the Retrived August.
Vasbieva, D., & Saienko, N. (2018). Exploring students' perception and efficiency of technology-mediated ESP teaching. XLinguae, 11, 127-137. doi:10.18355/XL.2018.11.01XL.11
Weaver. (1994). Reading Process and Practice: From socio-psycholinguistic to whole language. Portsmouth: Heinemann.
Yurdagül, C., & Oz, S. (2018). Attitude towards Mobile Learning in English Language Education. Education Sciences, 8, 142. doi:10.3390/educsci8030142
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Phayao University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยาไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย
The authors are themselves responsible for their contents. Signed articles may not always reflect the opinion of University of Phayao. The articles can be reproduced and reprinted, provided that permission is given by the authors and acknowledgement must be given.







