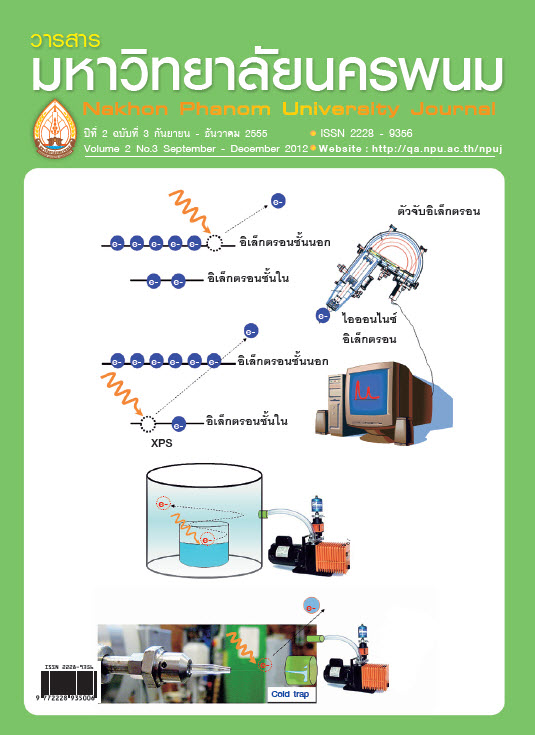
การใช้แสงซินโครตรอนศึกษาของเหลว ด้วยเทคนิคโฟโต้อิเล็กตรอนสเปกโทรสโกปี
Main Article Content
Abstract
ลิควิดไมโครเจ็ท (Liquid micro-jet) เป็นนวัตกรรมใหม่ ที่ถูกนำมาแก้ปัญหาการศึกษาสถานะของของเหลวในน้ำหรือสารละลายชนิดต่างๆ ในการทดลองด้านสเปกโทรสโกปี ด้วยคุณสมบัติเฉพาะตัวคือให้ลำของเหลวที่มีขนาดเล็ก จึงช่วยลดไอความดันในระบบ ประกอบกับการใช้ไนโตรเจนเหลวเป็นตัวจับและทำให้ลำของเหลวแข็งตัว จึงทำให้ความดันขณะทำการทดลองอยู่ในระดับเหมาะสม และจากการใช้ลิควิดไมโครเจ็ทในกระบวนการโฟโต้อิเล็กตรอนสเปกโทรสโกปีศึกษาพฤติกรรมของไอออนเดี่ยวและไอออนคู่ คือ โพแทสเซียมและแคลเซียมไอออน ซึ่งมีประจุ +1 และ +2 ตามลำดับ พร้อมทั้งเปรียบเทียบพฤติกรรมของไอออนทั้งสองในสารละลายโพแทสเซียมและแคลเซียมคลอไรด์พบว่า พลังงานยึดเหนี่ยวของอิเล็กตรอนในระดับชั้นพลังงานลึกของทั้งสองไอออนในสถานะของเหลวต่ำกว่าในสถานะก๊าซ ประมาณ 4 electron volt และเมื่อเปรียบเทียบระหว่างสถานะของแข็งและของเหลวพบว่า ในกรณีของแคลเซียมไอออนค่าพลังงานยึดเหนี่ยวของอิเล็กตรอนทั้งสองสถานะมีค่าใกล้เคียงกัน ขณะที่โพแทสเซียมไอออนในสถานะของเหลวมีค่าพลังงานยึดเหนี่ยวต่ำกว่าสถานะของแข็งประมาณ 3 electron volt เนื่องจากแคลเซียมไอออนมีประจุสูงกว่าจึงเกิดการโพลาไรเซชันได้ดีกว่าโพแทสเซียมซึ่งมีจำนวนประจุต่ำกว่า ซึ่งส่งผลถึงความสามารถในการดึงโมเลกุลของน้ำให้เข้าใกล้ไอออนได้มากกว่าเช่นกัน นั่นคือไอออนบวกที่มีจำนวนประจุสูงกว่าสามารถเกิดอันตรกริยากับโมเลกุลของน้ำที่อยู่บริเวณโดยรอบได้มากกว่าไอออนบวกที่มีจำนวนประจุ น้อยกว่านั่นเอง
Liquid micro-jet is a new innovation and recently it has been applied to photoelectron spectroscopy for studying liquid phase in water and aqueous solutions. Its characteristic; small size of the jet, reduces the vapour pressure. Together with combining liquid nitrogen in cold trap makes the experiment smoothly. We applied liquid micro-jet to study potassium and calcium cations in aqueous potassium and calcium chloride respectively. In comparison to those of the gas phase, the photoelectron spectra of both solvated ions are shifted to lower binding energy approximately 4 electron volt. However, the binding energy of the solvated calcium ion is identical to the solid salt, whereas the solvated potassium ion is lower than that 3 electron volt. This is attributed to the electronic polarization of the water molecules around an ionized calcium ion is stronger than potassium. In addition, the divalent cation (calcium = +2) has stronger interaction with surrounded water molecules than the monovalent cation (potassium = +1) due to the distance between the solvated ions and water molecule is shorter and stronger polarisation.