The Comparison of Data Classification Efficiency to Predict Scholarship Awarded for Undergraduate Students by Data Mining Techniques
Keywords:
Scholarship, Desicion Tree, Naive Bayes, K-Nearest Neighbors, Deep Learning, Random ForestAbstract
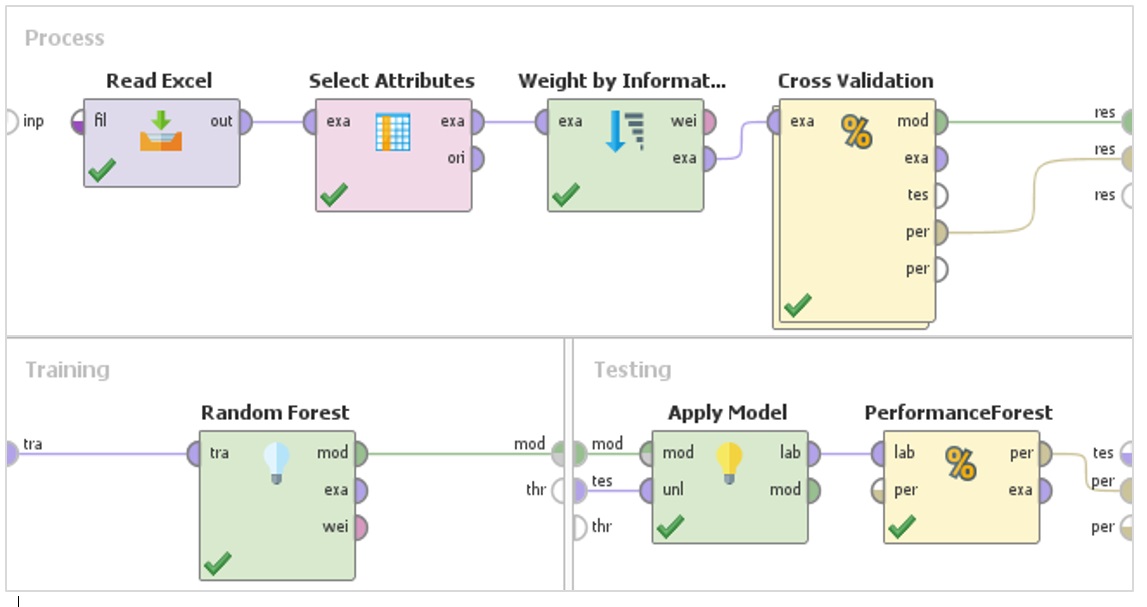
This research analyzed factors involved with the scholarship data of undergraduate students and compared the performance of data mining techniques used to analyze the data: Decision Tree, Naïve Bayes, K-Nearest Neighbors, Deep Learning and Random Forest. The data was collected from the scholarship form of undergraduate students in the Faculty of Business Administration and the Faculty of Art from Borpitpimuk Chakrawad Division, Rajamangala University of Technology Rattanakosin during 2014 to 2018 school years. The dataset had 15 attributes and 1,155 records. The RapidMiner Studio program was used to find the number of relations attributes and model, and the 10-Fold Cross Validation to evaluate the model. The results showed that 11 attributes were involved. The accuracy of Random Forest, Deep Learning, Decision Tree, Naïve Bayes and K-Nearest Neighbors were at 94.28%, 93.51%, 92.64%, 92.47%, and 89.70%, respectively. The research could be used to predict, to analyze recommendations and to develop an information system to support the decisions in awarding scholarships to students.
References
กองทุนเพื่อความเสมอภาคทางการศึกษา. รายงานประจำปี 2562. กรุงเทพฯ: กสศ.; 2563.
พลเดช ปิ่นประทีป. กองทุนเพื่อความเสมอภาคทางการศึกษา (กสศ.) เป็นเครื่องมือใหม่ที่มีความสำคัญต่อการลดความเหลื่อมล้ำและขับเคลื่อนการปฏิรูปประเทศด้านการศึกษาในระยะยาว [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อวันที่ 4 กุมภาพันธ์ 2564]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://www. eef. or.th/103/
ภูมิศรันย์ ทองเลี่ยมนาค. สำรวจผลกระทบ COVID-19 จุดเปลี่ยนครั้งสำคัญของการศึกษาโลก [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อวันที่ 4 กุมภาพันธ์ 2564]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://www.eef. or.th/article1-02-01-211/
วิภา เจริญภัณฑารักษ์. คลังข้อมูล เหมืองข้อมูลและธุรกิจอัจฉริยะ หน่วยที่ 8. นนทบุรี: สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยสุโขทัยธรรมาธิราช; 2558.
วัจนา ขาวฟ้า และ อรศิริ ศิลาลัย. แบบจำลองการเลือกสายการเรียนที่เหมาะสมของนักศึกษาด้วยเทคนิคการจำแนก. การประชุมวิชาการระดับชาติและนานาชาติ มหาวิทยาลัยศรีปทุม ครั้งที่ 14 ประจำปี 2562; หน้า 1485-93.
อดุลย์ ยิ้มงาม. การทําเหมืองข้อมูล(Data Mining) [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อวันที่ 5 กุมภาพันธ์ 2564]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://com pcente.bu.ac.th/news-information/data-mining/
สายชล สินสมบูรณ์ทอง. การทำเหมืองข้อมูล เล่ม 1 การค้นหาความรู้จากข้อมูล. กรุงเทพฯ: จามจุรีโปรดักส์; 2560.
Nutdanai Wangpratham. DATA PREPARA- TION การเตรียมข้อมูล [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อวันที่ 5 กุมภาพันธ์ 2564]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://nutdnuy.medium.com/datapreparation-การเตรียมข้อมูล-81fba4e0b0c9
นงคราญ คำวิชัย. Practical Data Mining with RapidMiner Studio 7. เชียงใหม่: ITSCI; 2559.
Kasidis Satangmongkol. อธิบาย 10 Metrics พื้นฐานสำหรับวัดผลดโมเดล Machine Learning [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อวันที่ 12 เมษายน 2564]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://datarockie. com/2019/03/30/top-ten-machine-learning-metrics/
วิริยาภรณ์ พิชัยโชคและจันทร์จิรา พยัคฆ์เพศ. การประยุกต์ใช้กระบวนการลำดับชั้นเชิงวิเคราะห์เพื่อพิจารณาทุนการศึกษาของโรงเรียนหัวดงราชพรหมาภรณ์ จังหวัดนครสวรรค์. NU Science Journal 2013:9(2):29-46.
ปิยะนันท์ คงไพ่, จิรพันธุ์ ศรีสมพันธุ์ และจรัญ แสนราช. การวิเคราะห์รูปแบบความสนใจเลือกอาชีพของผู้เรียนการแบบทดสอบ ตามทฤษฎีของจอห์น ฮอลแลนด์ ด้วยเทคนิคเหมืองข้อมูล. Science and Technology RMUTT Journal 2019;9:80-90.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
บทความทุกบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารการพัฒนางานประจำสู่งานวิจัย (JPR2R) ถือว่าเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารการพัฒนางานประจำสู่งานวิจัย คณะสิ่งแวดล้อมและทรัพยากรศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล





