The The Exercise Behaviors and Needs of the Customers at the Sports Center, College of Sports Science and Technology, Mahidol University, after the Pandemic of Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19)
Keywords:
exercise behaviors, sports center, the pandemic of Coronavirus (COVID-19), New NormalAbstract
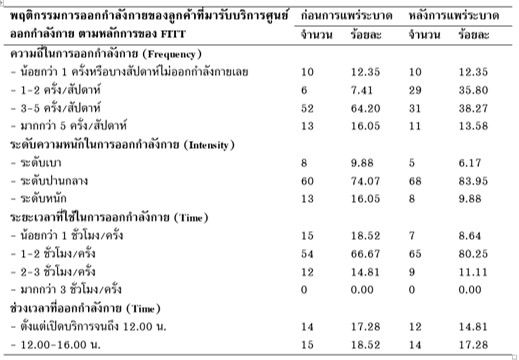
The research studied (1) the exercise behaviors of customers at the Sports Center before and after the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), (2) the needs for prevention measures after the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 – including the physical and environmental measures, monitoring and risk-screening measures, self-protection measures, and personal-spacing measures, (3) the cooperation of customers, and (4) their opinions about the Sports Center services after the pandemic with the new normal pattern. The data were collected by questionnaires during August – September 2020 from 81 customers at the Sports Center, College of Sports Science and Technology, Mahidol University, before analysis using frequency, percentage (%), mean ( ), and standard deviation (S.D.). The research found that exercise behaviors before and after the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are not different. The needs for the prevention measures at the Sports Center after the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is at a high level ( = 3.86). The need for the monitoring and risk-screening guideline is the most crucial ( = 3.98). Moreover, the cooperation of customers when using the Sports Center to prevent the pandemic is at the highest level with an average of 4.21, while their opinions about the post COVID-19 services of the Sports Center with a new normal concept is also at the highest level with an average of 4.00.
References
สุรัยยา หมานมานะ,โสภณ เอี่ยมศิริถาวร และ สุมนมาลย์ อุทยมกุล. โรคติดเชื้อไวรัสโคโรนา 2019 (COVID-19).วารสารสถาบันบำราศนราดูร 2563;14(2):E1-E10.
แบรนด์ อินไซด์. จุดพลิกอุตสาหกรรมฟิตเนส เมื่อ COVID-19 ทำการออกกำลังกายออนไลน์บูมจนยิมต่างๆ เริ่มมีปัญหา [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2563 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2563 ก.ค.31]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://brandinside.asia/fitness-future-covid-19/
มาลี บุญศิริพันธ์. รู้จัก "New Normal" ฉบับราชบัณฑิตยสภา [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2563 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2563 กรกฎาคม 10]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://news.thaipbs.or.th/content/292126
Best, J.W. Research in Education.10thed. Cape Town: Pearson Education Inc.; 2006
ไทยโพสต์. ยุคทองธุรกิจสุขภาพ [อินเทอร์เน็ต].2563 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 2563 มิถุนายน 2]. เข้าถึงได้จากhttps://www.thaipost.net/main/detail/ 67567.
อวาทิพย์ แว. COVID-19 กับการเรียนรู้สู่การปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพในวันนี้. วารสารสมาคมวิชาชีพสุขศึกษา 2563;35(1): 24-9.
กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.คู่มือปฏิบัติการตามมาตรการผ่อนคลายกิจการและกิจกรรมเพื่อป้องกันการแพร่ระบาดของโรคโควิด-19 สำหรับประเภทกิจการและกิจกรรม กลุ่มที่ 3. กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักพิมพ์อักษรกราฟฟิกแอนด์ดีไซน์; 2563.
Vardavas CI, Odani S, Nikitara K, Banhawi HE, Kyriakos CN, Taylor L et al. Perceptions and practice of personal protective behaviors to prevent COVID-19 transmission in the G7 nations. Population Medicine 2020;2(June):17.
Dryhurst S, Schneider CR, Kerr J, Freeman ALJ, Recchia G, Marthe van der Bles A et al. Risk perceptions of COVID-19 around the world. Journal of Risk Research. online: 05 May 2020 https://doi.org/10.1080/ 13669877.2020. 1758193.
ขวัญเมือง แก้วดำเกิง.พฤติกรรมของประชากรโลกในช่วงเผชิญภาวะวิกฤติ COVID-19.วารสารสมาคมวิชาชีพสุขศึกษา 2563;35(1):14-22.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
บทความทุกบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารการพัฒนางานประจำสู่งานวิจัย (JPR2R) ถือว่าเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารการพัฒนางานประจำสู่งานวิจัย คณะสิ่งแวดล้อมและทรัพยากรศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล





